In the world of business management, two terms that often come up when discussing people management are HCM (Human Capital Management) and HR (Human Resources). While these terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct differences, especially in their scope and application within organizations.
In this article, we will define HCM and HR, explore the key differences between the two, and understand how businesses can benefit from each.
What Does HCM Stand For?
Human Capital Management (HCM) refers to the comprehensive set of practices and technologies used by organizations to manage and optimize their workforce. The term “capital” in HCM refers to the value of the employees as assets to the company, focusing on how to maximize their potential, performance, and development. HCM includes various processes such as recruitment, training, performance management, compensation management, and employee engagement, all of which contribute to a company’s overall success.
HCM is a more strategic approach to managing employees, focusing on the long-term value they bring to the organization. It integrates multiple tools, technologies, and strategies to ensure the company’s human capital is being utilized efficiently and effectively.
What Is HR?
Human Resources (HR), on the other hand, traditionally refers to the department or function within an organization responsible for recruiting, hiring, training, and managing employees. HR has a broader focus on the administrative aspects of people management, such as ensuring compliance with labor laws, managing employee benefits, handling payroll, and resolving workplace conflicts. HR also plays a role in maintaining a company’s culture and ensuring that employees have a safe, healthy, and productive work environment.
While HR focuses on day-to-day operations and administrative tasks, it is often seen as a more tactical function rather than a strategic one. Over time, HR has evolved to encompass more elements of employee engagement, development, and retention, but its core focus remains on employee management and legal compliance.
Also Read: What does LMS Mean?
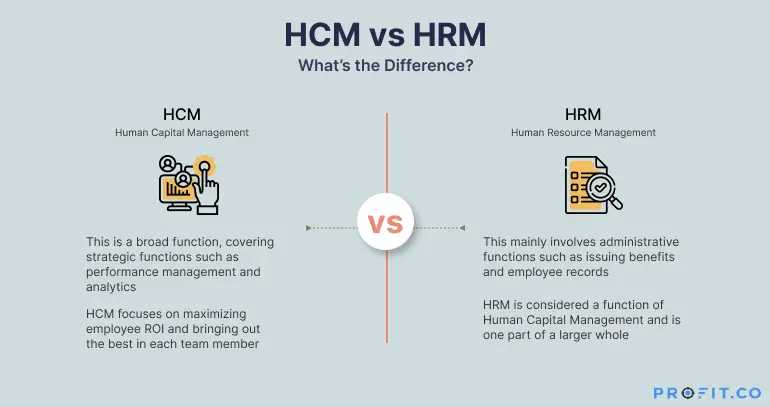
Key Differences Between HCM and HR
Source: Profit.co
While both HCM and HR involve managing the workforce, there are clear distinctions in their approaches, scope, and goals.
1. Scope and Focus
- HCM is a broader, more strategic approach. It is concerned with not only managing the workforce but also ensuring that employees are developed, engaged, and supported in ways that enhance their value to the organization. HCM goes beyond basic administrative tasks and aligns closely with organizational goals to drive performance and productivity.
- HR, in contrast, is typically more focused on the tactical and operational aspects of people management. HR ensures that the organization is compliant with regulations, handles the recruitment and onboarding process, and manages employee relations.
2. Strategic vs. Administrative
- HCM is a strategic function. It focuses on maximizing the value of employees over time by nurturing their skills, aligning them with company objectives, and developing leadership within the organization. It involves continuous feedback loops, performance management, and career development.
- HR is traditionally more administrative, handling the day-to-day operations of hiring, payroll, benefits, compliance, and dispute resolution. It is crucial for ensuring the smooth functioning of the organization but does not always take a long-term, strategic approach to employee development.
3. Technological Integration
- HCM relies heavily on technology and data to manage the workforce. It involves using software systems (like Workday, SAP SuccessFactors, or Oracle HCM) to manage everything from recruitment to performance evaluation, talent management, learning, and analytics. These tools help organizations make data-driven decisions that impact business growth.
- HR, while increasingly incorporating technology, traditionally does not use data and analytics as comprehensively as HCM. While HR systems might include HR software for tasks like payroll and benefits management, the integration of advanced analytics and talent management systems is typically more prominent in HCM.
4. Employee Engagement and Development
- HCM focuses significantly on employee development and engagement. It integrates training, career development programs, leadership development, and employee satisfaction to help employees grow within the company. HCM aims to optimize the potential of each employee, which is essential for long-term business success.
- HR, while involved in employee engagement, does not traditionally focus as deeply on employee development. Its focus is more on ensuring that employees meet compliance standards and are properly compensated and supported.
How HCM and HR Work Together?
Although HCM and HR have distinct differences, they must work in tandem to ensure a company’s human resources are being managed optimally. HR is essential for handling administrative tasks, legal compliance, and initial recruitment, while HCM ensures that the company maximizes the potential of its workforce over time.
By integrating HCM with HR, organizations can benefit from the best of both worlds. HR ensures that the organization remains compliant and operationally efficient, while HCM ensures that employees are engaged, developed, and aligned with the company’s long-term objectives.
Why Businesses Need Both HCM and HR?
Having both HCM and HR in place can provide tangible benefits for businesses:
- Improved Employee Engagement: A strategic focus on employee development and engagement through HCM leads to higher retention and satisfaction.
- Better Decision Making: HCM’s integration of data and analytics helps business leaders make informed decisions about their workforce.
- Compliance and Efficiency: HR ensures that the company remains compliant with labor laws and handles the operational side of human resource management efficiently.
- Long-term Growth: Combining the tactical strength of HR with the strategic foresight of HCM helps organizations build a robust, future-ready workforce.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both HCM and HR play critical roles in managing a company’s workforce, they serve different purposes within an organization. HCM is focused on strategically managing human capital to drive long-term success, while HR handles the day-to-day administrative responsibilities.
By understanding these differences and integrating both systems effectively, organizations can build a workforce that is not only compliant but also capable of achieving high performance and long-term growth.
